Offering enhanced connectivity and unprecedented broadband speeds, the industrial rollout of 5G technology is sparking a wave of predictions about its transformative potential in the healthcare industry. Particularly promising is its application in remote robotic-assisted surgery, paving the way for cross-country procedures that were once deemed impossible.
Medical device manufacturers are looking to capitalise on the immense market potential by heavily investing in medical robotic systems. Notable examples include Medtronic’s acquisition of Mazor Robotics, a spine surgery guidance systems developer, for a staggering $1.64 billion, and Johnson & Johnson’s $3.4 billion deal to acquire Auris Health, a Silicon Valley-based designer of endoscopic hardware targeting lung cancer.
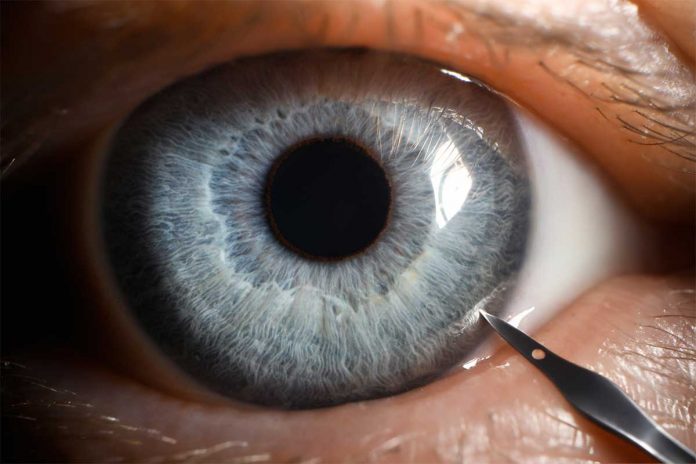
In China, the Zhongshan Ophthalmic Centre at Sun Yat-sen University are reported to have already achieved a groundbreaking milestone in ophthalmic surgery by successfully conducting the world’s first remote, micron-level surgery on rabbits using a self-developed 5G robot. The trailblazing surgeries took place on June 23 in Guangzhou, Guangdong province, with the surgical team operating the robot from the Hainan Eye Hospital at Zhongshan Ophthalmic Centre in Haikou, Hainan province.
The milestone was led by Professor Lin Haotian’s team, and all 12 rabbits that underwent surgery are reportedly in stable condition after a month of observation. Professor Lin, the director of Zhongshan Ophthalmic Centre, expressed confidence that this breakthrough will accelerate remote medicine in China, elevating the country’s medical devices and equipment to global leadership levels, while also contributing to the development of national medical standards.
Furthermore, the achievement holds far-reaching implications for addressing the disparities in ophthalmology development and uneven distribution of medical resources across the country. By saving time for doctors and patients, reducing economic costs, and enhancing treatment efficiency, telemedicine powered by 5G has the potential to overcome these challenges.
Professor Lin revealed an ambitious timeline, stating that if all progresses smoothly, 5G remote micron ophthalmic surgery could become available for human patients within half a year.
While the potential for 5G networks enabling near-instantaneous communication is undeniable, there are challenges to overcome. One significant hurdle for mass adoption and widespread usage lies in the requirement for haptic feedback in robotic-assisted surgeries. Manufacturers are actively exploring ways to incorporate haptic feedback into their devices, recognizing its importance for surgical precision.
Industry experts predict that the first major surgical robotics company to integrate haptic feedback will capture a substantial market share, likely driving fierce competition in the surgical robotics industry.
As the 5G revolution in healthcare continues to unfold, the possibilities for advancements in remote surgery and medical technology are limitless, bringing hope for a new era of healthcare innovation.
Related article: WeChat Pay Opens Doors for International Tourists: How to Link Visa Cards for Seamless Transactions